A recent project reported in the journal Physical Review Letters showcased a new type of small, highly sensitive gravimeter developed by a team of physicists and engineers in China. This gravimeter can operate at room temperature, overcoming some of the limitations of earlier gravity measurement devices. The team utilized a dual magnet strategy along with a laser to accurately measure changes in gravity.
Traditional gravity measurement devices have faced challenges such as aging quickly and requiring cold containers. Devices based on small oscillators tend to lose precision over time, while those relying on superconducting materials are not only power-intensive but also difficult to move due to the need for cold containers. These limitations have prompted the need for a more innovative and efficient approach to gravity measurement.
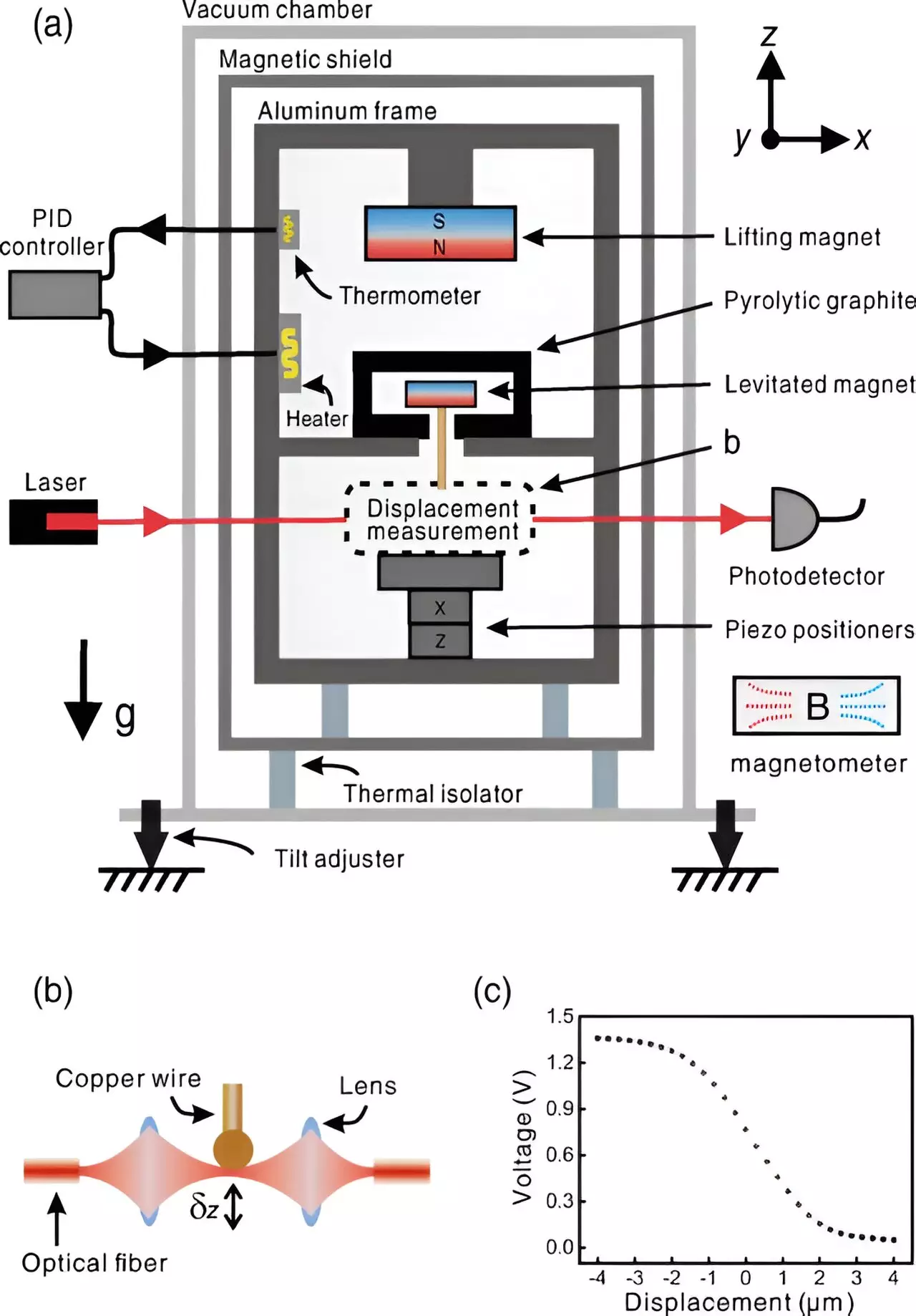
The team’s new gravimeter features a large magnet inside a cabinet attached to its top, with a smaller magnet beneath it enclosed in a field-repelling graphite shell. The opposing magnetism causes the smaller magnet to levitate, resulting in vertical oscillations that can be fine-tuned by adjusting the space between the magnets. Additionally, a wire hanging down from the larger magnet allows for the measurement of changes in gravitational pull. A vertical laser detects the intensity variations as the wire blocks its path, enabling precise calculation of the amount of gravity experienced by the device.
To evaluate the performance of their device, the team placed it in a vacuum chamber for several weeks to stabilize. Subsequently, they conducted gravity measurements from the moon and sun over five days, comparing the results with predicted values. The team observed oscillations in the signal representing variations in gravitational acceleration up to about 10^-7 of the standard value, indicating high accuracy. They consider this work a proof-of-concept and anticipate further refinements to enhance precision. Future plans include improving the device’s physical robustness to facilitate mobility between different locations, ensuring its practicality and reliability in various settings.
The development of this small, highly sensitive gravimeter represents a significant advancement in gravity measurement technology. By addressing the limitations of previous devices and introducing innovative design elements, the research team has laid the foundation for more accurate and portable gravity measurement solutions in the future.

Leave a Reply