The field of medical imaging is constantly evolving, with researchers at the Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences making significant advancements in X-ray imaging technology. Their recent collaboration with researchers at Central China Normal University has led to the development of a high-performance perovskite X-ray complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) detector for medical imaging, as reported in a study published in Nature Communications on Feb. 21.
X-ray imaging plays a crucial role in the diagnosis and treatment of various diseases, such as cardiovascular and cancer. While direct-conversion X-ray detectors made of semiconductor materials offer superior spatial and temporal resolution at lower radiation doses compared to indirect-conversion detectors, the currently available semiconductor materials have limitations in terms of X-ray absorption efficiency and cost. This has led researchers to explore alternative materials, such as perovskite, for use in X-ray detectors.
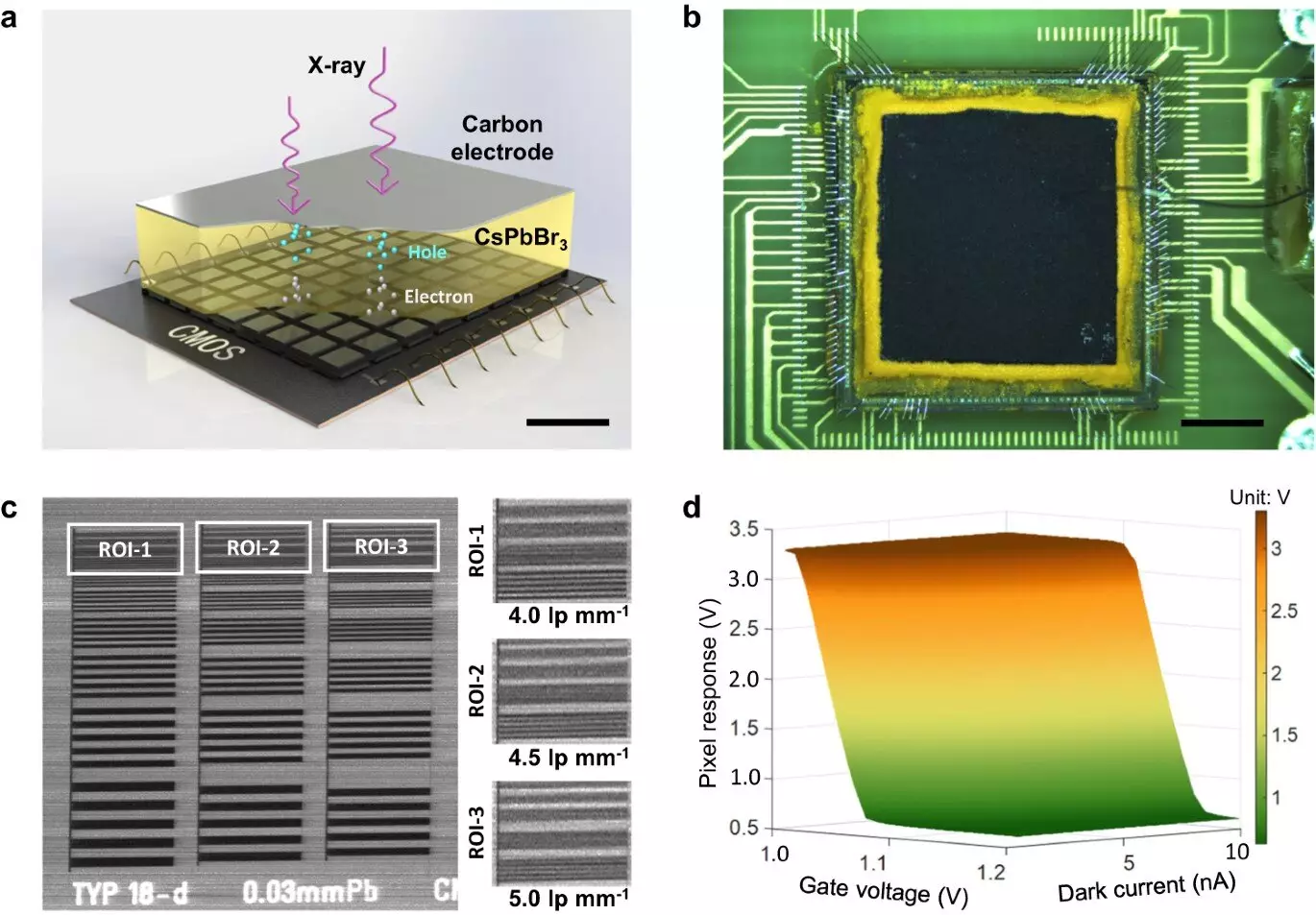
In their study, researchers developed a direct-conversion X-ray detector using a 300 µm thick inorganic CsPbBr3 perovskite film printed on a dedicated CMOS pixel array. The thick CsPbBr3 film exhibited high X-ray detection sensitivity, a low dose detection limit, and a high µτ product, making it a promising candidate for X-ray imaging applications. Experimental results demonstrated the detector’s high spatial resolution and low-dose imaging performance, showcasing its potential in revolutionizing X-ray imaging technology.
The successful development of the perovskite CMOS detector represents a significant advancement in X-ray imaging technology. With enhanced spatial resolution, readout speed, and low-dose detection efficiency, the detector offers the possibility of improving the accuracy and efficacy of diagnostic imaging procedures. Prof. Ge, leading the research team, highlighted the potential of lead halide perovskites in transforming the development of state-of-the-art X-ray detectors, paving the way for future innovations in medical imaging technology.
The collaboration between SIAT and Central China Normal University has led to the creation of a groundbreaking perovskite CMOS detector that shows great promise in revolutionizing X-ray imaging capabilities. By addressing the limitations of traditional semiconductor materials, this innovative detector offers enhanced performance and efficiency in medical imaging, opening up new possibilities for the diagnosis and treatment of various diseases.

Leave a Reply