Optical spectrometers have long been hailed for their versatility in producing light and measuring its properties across the electromagnetic spectrum. These instruments have found applications in various fields, ranging from medical diagnostics to material characterization. However, traditional spectrometer designs have been characterized by their bulkiness and high cost, limiting their deployment to specialized facilities. In recent years, efforts have been made to develop more compact and cost-effective optical spectrometers that could be easily deployed on a larger scale.
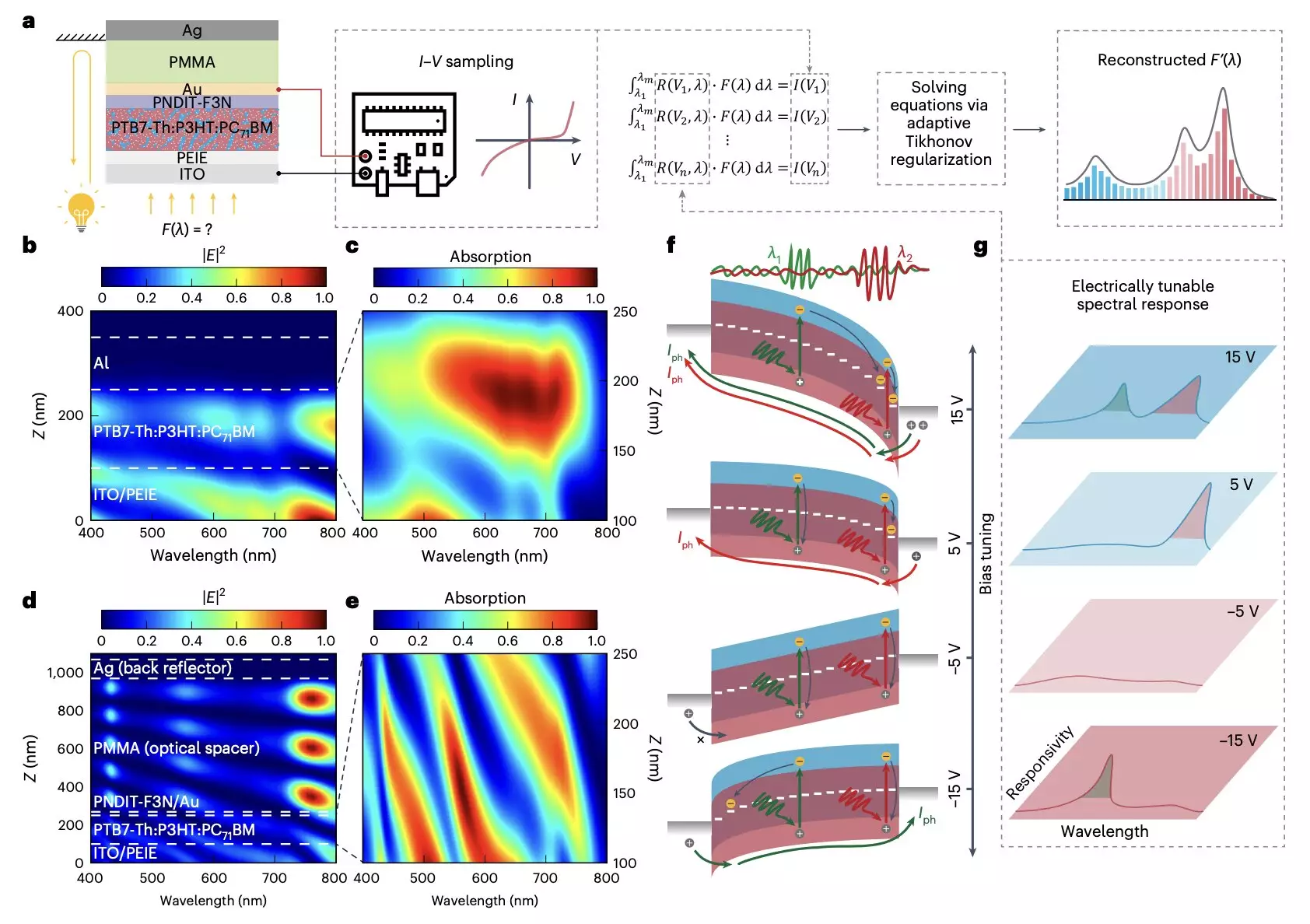
Researchers at the Chinese University of Hong Kong and other institutes in China have recently introduced a groundbreaking micro-sized optical spectrometer. This device, based on an organic photodetector with a bias-tunable spectral response, offers a portable and cost-effective alternative to conventional spectrometers. The spectrometer leverages a newly introduced method to manipulate the wavelength-dependent location of photocarrier generation in photodiodes, employing a trilayer contact, Schottky diode, and organic ternary bulk heterojunction. This innovative design allows for the computational reconstruction of incident light spectra with a footprint of just 0.0004 cm2, operating across the visible wavelength with sub-5-nm resolution.
The miniaturized optical spectrometer underwent rigorous testing, demonstrating exceptional results across the entire visible spectrum regime with sub-5-nm resolution. To further showcase its capabilities, the researchers utilized the spectrometer to fabricate an 8 x 8 spectroscopic sensor array for hyperspectral imaging. This technique enables the detection of unique spectral signatures of specific objects by processing information across the electromagnetic spectrum. The successful performance of this new optical spectrometer paves the way for the development of similar micro-sized and more affordable devices that could revolutionize research and medical practices.
The advances made in miniaturizing optical spectrometers hold immense promise for the future of spectroscopy. These compact and cost-effective devices could facilitate their integration into portable and wearable applications, expanding their utility beyond traditional laboratory settings. Moreover, the computational algorithms used in the reconstruction of light spectra offer a novel approach to spectrometer design, potentially inspiring the development of other sophisticated technologies. As such, the introduction of micro-sized optical spectrometers opens up new avenues for scientific research and medical advancements.
The development of a micro-sized optical spectrometer represents a significant breakthrough in the field of spectroscopy. By leveraging innovative design principles and computational algorithms, researchers have created a portable and cost-effective alternative to conventional spectrometers. The successful performance of this miniaturized device across the visible spectrum with high resolution underscores its potential for revolutionizing research and medical practices. As advancements in optical spectrometers continue to evolve, we can expect to see a new era of cutting-edge technologies that propel scientific discovery to new heights.

Leave a Reply