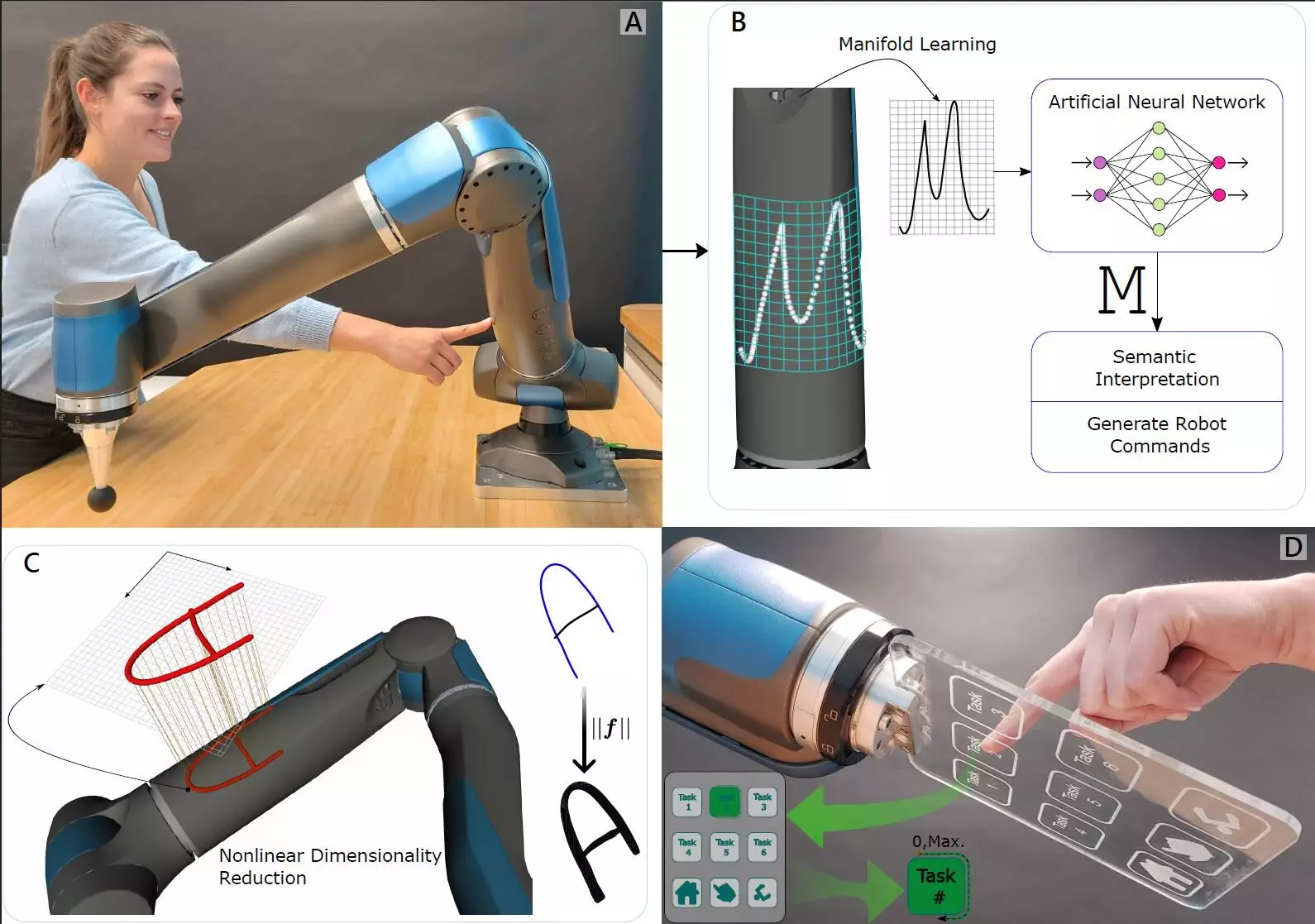
In a groundbreaking study led by roboticists at the German Aerospace Center’s Institute of Robotics and Mechatronics, the traditional understanding of tactile sensation in robots has undergone a profound transformation. Recognizing the complex nature of touch—not just the ability to feel, but to interpret interactions—researchers have developed a novel methodology that diverges from conventional artificial skin technologies. Their work, recently published in the prestigious journal Science Robotics, introduces a remarkable synergy between internal force-torque sensors and machine-learning approaches, granting robots a sophisticated form of touch perception.
Simulating Human-Like Touch
Touch for living beings is inherently a reciprocal experience, where sensation is influenced by both external stimuli and the dynamic context of interaction. The research team ingeniously mimicked this bi-directional aspect of touch in robotic systems by incorporating ultra-sensitive force-torque sensors into the robot’s joints. These state-of-the-art sensors are capable of detecting pressure from multiple angles, thereby allowing the robot to experience tension akin to that in human joints. This innovative design highlights an essential step towards enabling robots to interpret the subtleties of their physical interactions with the environment.
Machine Learning: The Game Changer
What sets this research apart is the application of machine learning to decode and contextualize the data collected by the force-torque sensors. By feeding the robot various scenarios and touch inputs, the machine-learning algorithm develops the capability to recognize distinct types of touch and pressure patterns. Imagine a robot not only aware of the sensation of fingers pressing against its arm but also capable of discerning the significance of these interactions, such as identifying which number was invoked when pressure was applied. This advancement signals an unprecedented leap in human-robot interaction, moving beyond mechanical responses to a more nuanced understanding.
A Future of Intuitive Interactions
The implications of this research are vast. As robots become increasingly integrated into industrial spheres, particularly in environments where they interact closely with humans, the necessity for nuanced touch capabilities cannot be overstated. Enhanced touch perception allows robots to work alongside humans more effectively and safely, improving productivity and promoting collaborative efforts. No longer limited by rigid programming or unresponsive artificial skins, these robots could evolve into empathetic partners, equipped to respond intelligently to human interactions.
Through this innovative approach, scientists are not merely improving robotic capability; they are redefining the potential of machines to engage with the world around them. The movement toward smarter and more touch-aware robotics raises essential questions about the future of collaboration between humans and machines. As we embrace this technology, we stand on the brink of a new era where robots understand and respond to touch in ways we are just beginning to explore.

Leave a Reply