In an increasingly digital world, the dynamics of communication are evolving rapidly. Traditional social media interactions are being redefined by technological innovations, particularly through the advent of virtual avatars. This trend is gaining traction amongst major platforms, exemplified by Meta’s CEO Mark Zuckerberg’s recent assertions regarding the rise of AI-generated interactions. According to Zuckerberg, augmented reality and artificial intelligence are pivotal to the future of social engagement, a viewpoint that finds resonance in Meta’s ongoing initiatives to integrate generative AI technologies into its ecosystem.
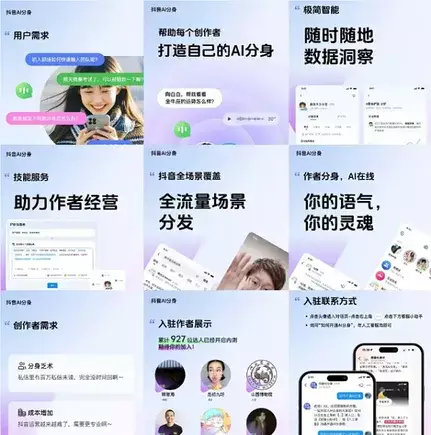
Zuckerberg’s vision does not exist in a vacuum. Rival platforms like TikTok are joining the fray, launching parallel innovations to enhance user engagement. Douyin, the Chinese counterpart to TikTok, is embarking on an ambitious project known as “Project V,” which aims to broaden the scope of live streaming and user interaction. Central to this project is an AI Avatar feature, designed to allow creators to forge virtual personalities that faithfully reflect their unique perspectives. This capability promises to maintain a constant connection between creators and their audiences, effectively enabling asynchronous interaction driven by AI.
Douyin’s AI avatars capture the ability of creators to engage continuously with users, effectively creating a dynamic, 24/7 interaction model. Users are able to converse with avatars that mirror the creators’ personalities, obtaining insights and responses even in the absence of the creators themselves. This innovation is a significant leap in the realm of digital interaction, essentially blurring the lines between human presence and AI mimicry. It is reminiscent of Meta’s strides in developing video avatars, which capitalize on users’ previous content to create digital representations capable of engaging with others on their behalf.
Furthermore, Douyin’s experience in the realm of virtual avatars is noteworthy. The platform has successfully employed digital avatars for live shopping streams, showcasing their utility and effectiveness in real-time commerce. The proliferation of digital avatars in China, evidenced by almost a million registered avatar companies, highlights the burgeoning demand for virtual influencers capable of operating autonomously across multiple channels. However, it raises a crucial question: Will the Western audience embrace similar technologies?
The disparity in cultural receptivity between Eastern and Western markets poses significant challenges for the acceptance of virtual avatars in platforms like TikTok. Historical trends suggest that many features that gain traction in China do not necessarily resonate with U.S. audiences. For instance, the shopping functionality within TikTok has faced hurdles, signaling that engagement strategies effective in one market may falter in another.
Critically, while the technological advancement of avatars may be appealing, the essence of social media has primarily revolved around authentic human interactions. Although AI bots provide a semblance of connectivity, they lack the intrinsic human qualities necessary for genuine dialogue. Engagement driven by avatars—no matter how lifelike or innovative—may be perceived as disingenuous, ultimately detracting from the authentic experiences that platforms like Instagram and Twitter aim to offer.
The Allure of Authenticity in Social Media
A key appealing factor of social media platforms lies in the potential for direct, sometimes unfiltered, engagement with individuals of prominence. The prospect of tagging a celebrity or public figure and potentially receiving a response creates a unique sense of connection that is fundamentally undermined by the presence of AI bots. Instead of fostering genuine dialogue, virtual representations can lead to an artificial form of interaction that may disappoint users looking for real connections.
While AI-generated templates and avatars can serve as useful tools for repetitive engagement—such as responding to FAQ-style inquiries—they do not replace the value of interacting with real humans who can respond to nuanced queries. The current popularity of conversational AI, like ChatGPT, suggests that people seek intellectual collaboration with bots in specific contexts. However, translating that utility into social interactions on platforms designed for personal engagement remains contentious.
Despite skepticism regarding their long-term appeal, the proliferation of AI avatars suggests a growing acceptance of digital alter egos in various capacities. Users today are increasingly drawn to metrics like likes, shares, and follower count, potentially leading to a decreased emphasis on the authenticity of interactions. The future might reveal a landscape where consumers become accustomed to engaging with avatars, blurring the line between human and machine-led communication.
The potential for virtual avatars to become ubiquitous in online engagement leaves significant implications for the social media landscape. Whether these innovations cultivate a more meaningful or superficial online environment remains to be seen. While the allure of novelty and convenience may prove compelling, the fundamental essence of social interactions could be at stake, prompting a broader conversation about the future of connection in an increasingly digitized world.

Leave a Reply