Recent research conducted by RIKEN physicists has brought to light the fascinating concept of using magnetic fields to engineer flat bands in twisted graphene layers. This discovery has opened up a whole new realm of possibilities for exploring exotic physics in graphene, a material already known for its unique properties.
Graphene, a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, has long been recognized for its remarkable properties. Electrons in graphene move as if they have no mass, making it an ideal candidate for creating advanced electronic devices with capabilities beyond traditional silicon-based technology. However, when multiple layers of graphene are stacked and twisted, the properties become even more intriguing.
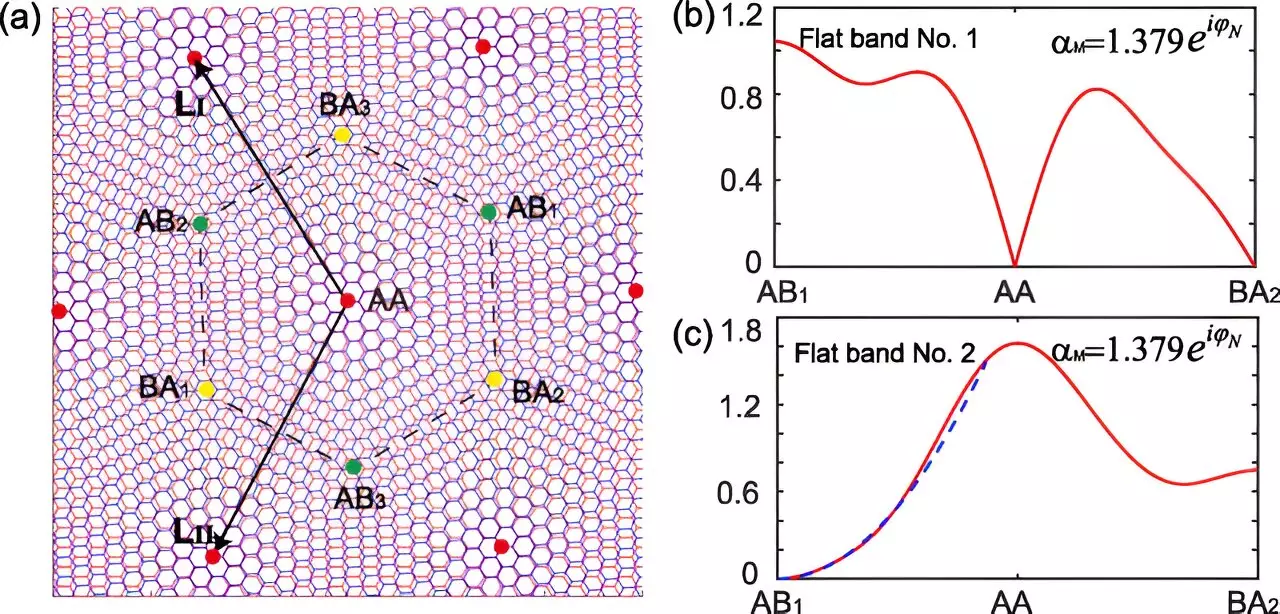
In the study led by Ching-Kai Chiu and Congcong Le from RIKEN, the researchers demonstrate that by applying a spatially varying magnetic field to twisted bilayer graphene, it is possible to create additional flat bands with quadruple degeneracy. This manipulation of the band structure opens up new opportunities for exploring correlated electronic phenomena, such as unconventional superconductivity.
Implications for Future Research
The discovery of these quadruply degenerate flat bands has undoubtedly sparked interest within the physics community. The potential for uncovering even more correlated phenomena by leveraging the magnetic phase as a novel degree of freedom is both exciting and groundbreaking. Researchers are now tasked with identifying other materials that exhibit similar properties, with the goal of expanding the scope of this research and delving deeper into the world of exotic physics.
The influence of magnetic fields on twisted graphene layers represents a significant advancement in our understanding of the behavior of electrons in condensed matter systems. By harnessing the power of magnetic manipulation, researchers have unlocked a vast playground for exploring exotic physics and discovering new electronic phenomena. The future of graphene research holds immense promise, as scientists continue to push the boundaries of what is known and explore the untapped potential of this extraordinary material.

Leave a Reply