X-ray bursts (XRBs) are powerful explosions that take place on the surface of a neutron star as it captures material from a nearby companion star. These explosions trigger a series of thermonuclear reactions that generate heavy chemical elements. A recent study published in Physical Review Letters delves into one specific reaction, the 22Mg(α,p)25Al reaction, shedding light on its significance in the context of XRBs.
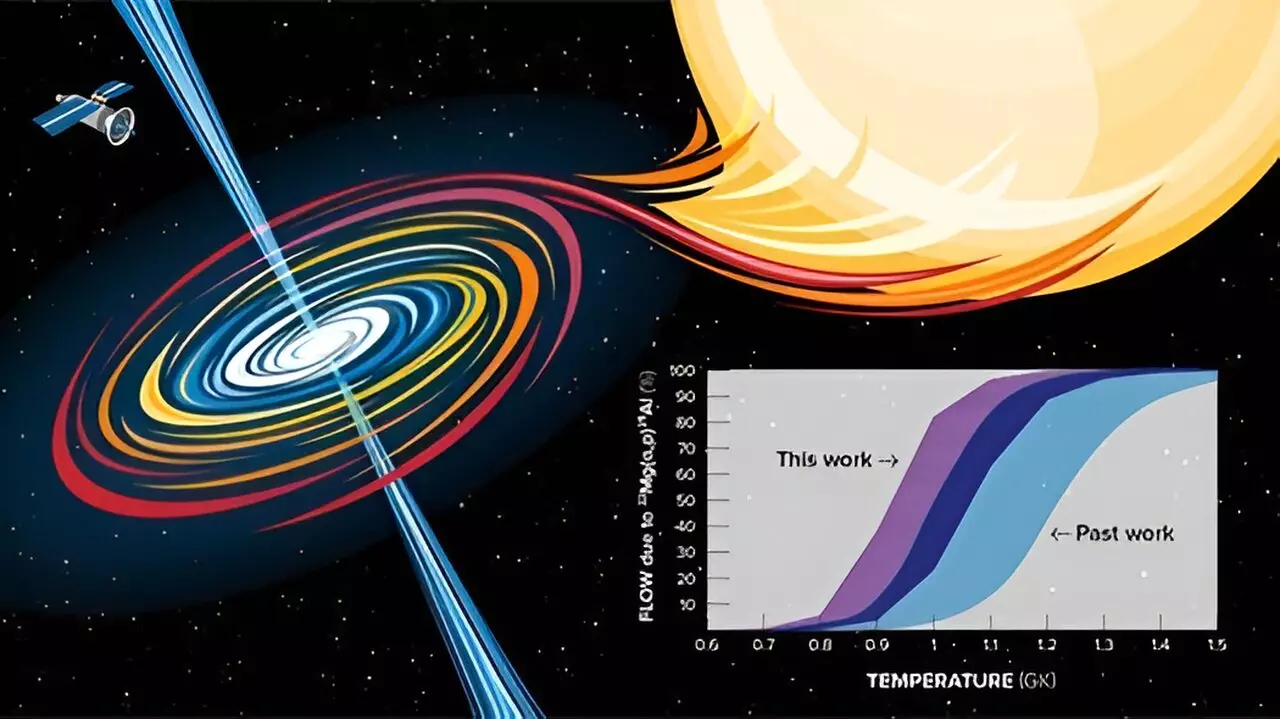
The 22Mg(α,p)25Al reaction is crucial in understanding the mechanisms behind XRBs and the factors that drive these explosions. By investigating this reaction, scientists can gain valuable insights into the synthesis of heavy elements during XRB events. The rate of this reaction influences the overall reaction flow through the 22Mg waiting point, a key stage in the nucleosynthesis process within XRBs.
To measure the 22Mg(α,p)25Al reaction, researchers conducted experiments using the Argonne Tandem Linac Accelerator System (ATLAS) at the Argonne National Laboratory. They utilized an in-flight radioactive beam and the MUlti-Sampling Ionization Chamber (MUSIC) detector to simulate conditions relevant to XRBs. The experiment resulted in a new direct measurement of the reaction’s cross-section, indicating a significantly higher probability of occurrence compared to previous measurements.
The findings from this study have significant implications for our understanding of XRBs. The increased rate of the 22Mg(α,p)25Al reaction suggests a more efficient bypassing of the 22Mg waiting point, leading to the continued synthesis of heavier elements. Moreover, the discovery that the reaction initiates at lower temperatures than previously believed offers new insights into the underlying physics of nucleosynthesis reactions in XRBs.
The investigation of the 22Mg(α,p)25Al reaction provides valuable information for enhancing our knowledge of XRBs and the processes that govern these explosive events. By refining our understanding of reaction rates and mechanisms in XRBs, scientists can further unravel the mysteries of neutron stars and the role they play in the synthesis of elements in the universe.

Leave a Reply