The field of solar cell research has been rapidly evolving over the past few years, with a particular focus on the development of organic solar cells based on perovskite materials. These organic solar cells have shown great promise, offering advantages such as lower fabrication costs, increased flexibility, and tunability. However, despite these benefits, the efficiency and stability of organic solar cells still lag behind those of conventional silicon-based designs.
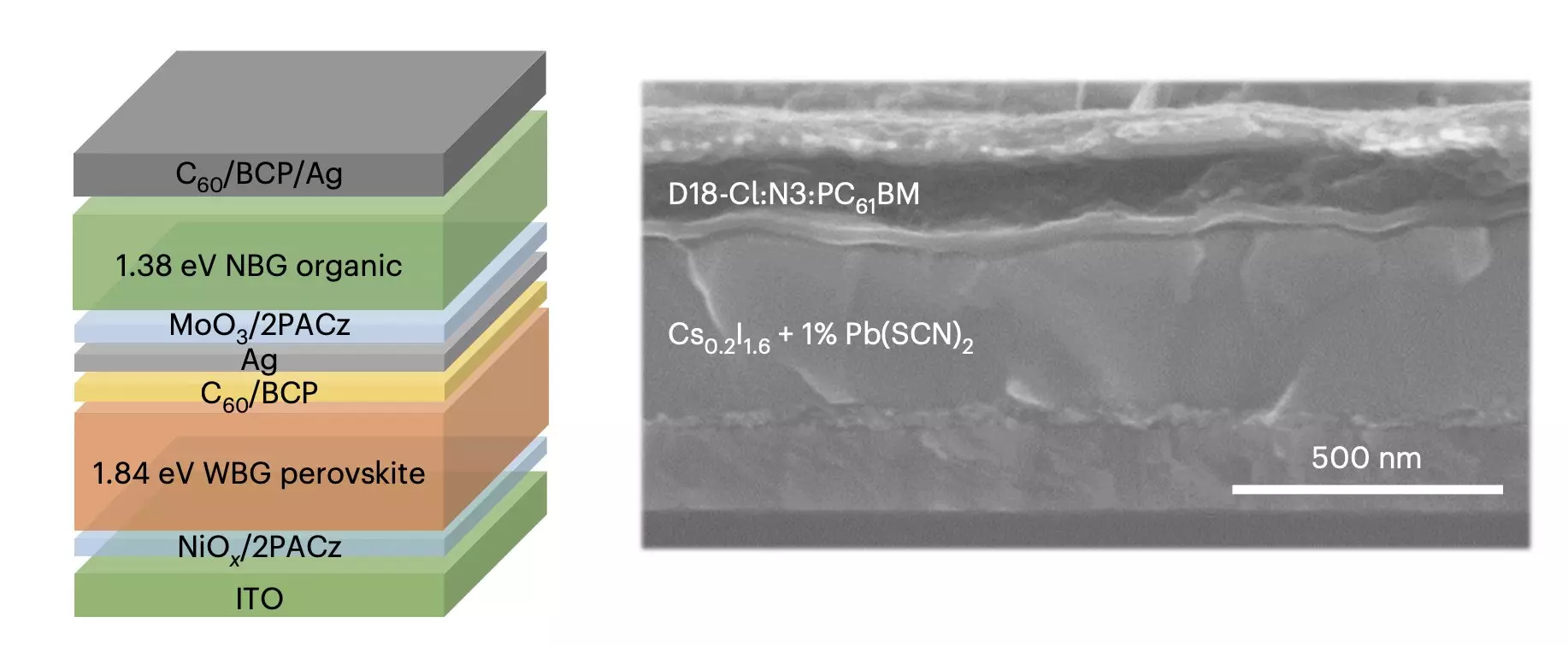
One of the main challenges facing organic solar cells is the issue of phase segregation in wide-bandgap perovskites. This process degrades the performance of the cells and hinders recombination processes at the interconnecting layer of tandem solar cells. To address this issue, researchers at Soochow University’s Suzhou Key Laboratory of Novel Semiconductor-optoelectronic materials and devices have devised a novel strategy to suppress phase segregation in wide-bandgap perovskites.
The researchers’ solution involves incorporating a pseudo-triple-halide alloy into mixed halide perovskites based on iodine and bromine. By introducing thiocyanate ions into the perovskite lattice, the researchers were able to prevent halide elements from separating inside the solar cells. This, in turn, slowed down crystallization and facilitated the movement of electric charge within the cells.
Initial tests of the researchers’ strategy showed promising results, with the resulting perovskite/organic tandem solar cells achieving a high power conversion efficiency of 25.82% and demonstrating operational stability over 1,000 hours. These findings suggest that the methodology introduced by Zhang, Chen, and their team could be applied to a wider range of wide-bandgap perovskites with different compositions, leading to the development of more stable and efficient solar cells in the future.
The combination of perovskite and organic solar cell designs shows great potential for the future of solar energy generation. By addressing key challenges such as phase segregation in wide-bandgap perovskites, researchers are paving the way for the development of high-efficiency, stable solar cells that can operate effectively under varying conditions. As the field continues to advance, we can look forward to more innovations and breakthroughs that will bring us closer to a sustainable and renewable energy future.

Leave a Reply